Look at your mobile device, your high-definition television, or laptop computer; what do you see? Most likely it’s a rectangular widescreen, with a lot of the video you watch on it filling the entirety of the screen. We are of course talking about the 16:9 ratio, which has been the current standard in television and monitors since at least the mid-2000s. But what is 16:9 aspect ratio, where did it come from, and how did it become the new default?
What is 16:9 aspect ratio
Defining the 16:9 ratio
Before getting into the intricacies of 16:9 resolutions, where it came from, and why it’s used, we want to provide a nice and easy definition. This definition will apply to the 16x9 aspect ratio across the board and prepare you for when we get into greater detail about its origins and usage.
16:9 DEFINITION
What is 16:9 Aspect Ratio?
The 16:9 aspect ratio is used in film and television and is used to describe an image that is 16 units wide by 9 units long. Also pronounced sixteen-nine, sixteen-to-nine, sixteen-by-nine, or 16 by 9. Also known as 1.77:1/1.78:1, this aspect ratio was developed in the 1980s and ‘90s. It became the default for high-definition television sets, screens, and monitors since the 2000s. Like 4:3, 16:9 typically — if not exclusively — refers to TV screens and monitors, as the more technical 1.77:1 (or rounded 1.78:1) specifically refers to celluloid and film/TV productions.
Characteristics of 16:9
- Rectangle widescreen display
- Made for high-definition video
- Displays higher quality imagery in many aspect ratios
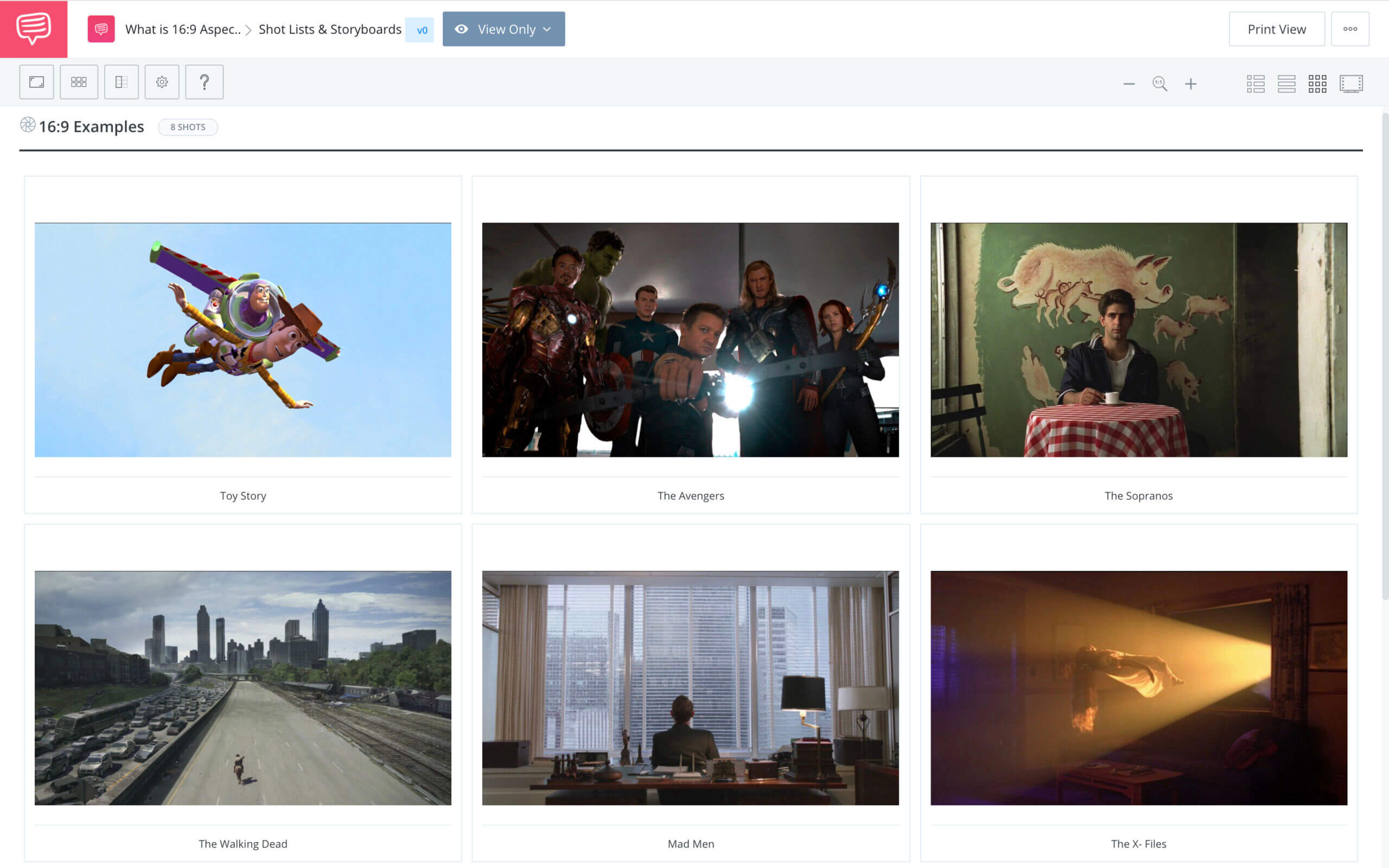
Using StudioBinder’s storyboard software, we can see multiple examples of various works in the 16x9 aspect ratio, some of which are movies and others which are iconic television shows.
16:9 screen ratio
A brief history of 16:9
Unlike its counterpart, 4:3, 16:9’s origins do not directly come from filmmaking limitations or technology of the time. Not unlike what Vittorio Storaro was trying to do with the 2:1 aspect ratio, 16:9 was meant to be the perfect aspect ratio that could accommodate the various ratios already in existence.
And this decision didn’t come from movie execs, but rather scientists trying to figure what the next great thing in monitors was going to look like. In other words, the 16:9 format was a future proofing ratio that could be implemented early before widespread adoption.
Thought up by Dr. Kerns H. Powers of SMPTE (Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers), the 16:9 ratio was created from a variety of mathematical equations and processes. He essentially concluded that it was the best option for the future of high-definition displays.
You can get an idea of what 16:9 aspect ratio resolutions mean to modern HD displays in the video below.
What is 16:9 aspect ratio? • A fast definition
Within this rectangle of a ratio, the 16:9 format allowed for ratios as square as 1.37 (also known as the 4:3 aspect ratio) and as wide as 2.39 (originally known as CinemaScope) to fit comfortably within its frame.
Additionally, ratios close to 16:9 resolutions, like 1.66 and 1.85, could fit very comfortably within a 16:9 screen ratio. In some cases, 1.66 or 1.85 would fit the entirety of the 16:9 ratio, either through cropping or opening up the natural image for home video release.
Otherwise, these ratios were pillarboxed (black panels on the sides of the screen) or letterboxed (black bars on the top and bottom of the screen). And in the case of DVD, movies could be formatted for widescreen televisions, no matter their aspect ratio, with the power of pillarboxing and letterboxing (and the removal of pan-and-scan).
While it began as a compromise, the 16x9 aspect ratio would soon dominate our high-definition landscape, with HD TVs becoming more and more popular in the mid-2000s.
By the end of the 2000s, 4:3 TVs were the old way, and this was further accelerated with HD Blu-ray discs and the HD video game consoles like Xbox 360 and PlayStation 3. Fast-forward a few years later, and now virtually everything is available in high-definition.
Related Posts
16:9 aspect ratio resolutions
16:9 in action
While 16:9 is now a standard, it can sometimes be tricky to understand what uses the 16:9 format, besides television sets and computer monitors. After all, movies still have their strict aspect ratios that are still the standard in both filmmaking and distribution to theaters. Our video below can fill you in on the various cinematic aspect ratios that exist.
What is 16:9 aspect ratio? • Subscribe on YouTube
1.85:1 is still the standard “flat” ratio used in many parts of the filmmaking world. This means that, if you watch a 1.85 movie on your 16:9 screen, slim black bars will appear at the top and bottom of the screen.
That said, most movies in 1.85 (and even a few in 2.39) are or have been shot “open matte,” meaning that the full image is closer to 4:3. This means many movies originally shot for 1.85 can be “opened up” when being presented on a 4:3 or 16:9 display, so that there is no letterboxing, which also means getting a little bit more visual information at the top and bottom of the frame.
The video below gives you an idea of how open matte is often used, especially in the case of 4:3. While 16:9 makes it easier to just show 1.85 movies in that ratio, some filmmakers might decide to open up the frame just a bit to fill in that extra space.
What is 16:9 aspect ratio? • DVD cropping
If you’re shooting a movie with modern digital technology, there is a good chance you can frame it in virtually any ratio you want. You can stick to 4:3, stay in 16:9 (like many a YouTuber), or go even wider. With HD cameras and displays, just about any ratio can be better displayed and shown.
The world of TV is easily where the 16:9 ratio shines, as many television programs will be shot and presented in a native 16:9. This is especially true of major network and cable channels, from CBS and NBC to HBO and Showtime. Streaming platforms like Netflix will vary, as they tend to have more creative freedom and leeway.
Even before 16:9 was everywhere, many TV shows in the 1990s and 2000s were shot with a 1.77 aspect ratio in mind, making it easy to broadcast in 4:3 at the time and then later in 16:9 on home video and streaming.
What is 16:9 aspect ratio? • Futureproofing
And we of course can’t forget the influence video games had in making 16:9 resolutions the standard. As early as the PlayStation 2, video game makers knew HD was the future. The Xbox 360, released in 2005, was the first major home console to have HD capability, followed by the PlayStation 3 (which came out one year after the 360). By the early 2010s, every major video game console was in native HD (with Nintendo finally getting there with the Wii U in 2012).
These days, your mobile phone is, if nothing else, in widescreen, thanks to the influence of 16:9 everywhere else. It’s still early innings, all things considered, but the 16:9 screen ratio has made a definite impact on how we watch and experience entertainment. It’s hard to say what can top it, but for now, it serves as the true compromise SMPTE envisioned it to be.
UP NEXT
Why today's filmmakers prefer 2:1
Now that you know a bit more about 16:9, why not learn a bit more about 2:1? Our article, with video, digs into the origins of 2:1, who uses it, and how it has popped up in more movies and shows in the last decade.
Up Next: What is 2:1? →
Showcase your vision with elegant shot lists and storyboards.
Create robust and customizable shot lists. Upload images to make storyboards and slideshows.